From Fingerprint to Face Recognition: The Rise of Biometric Security

Introduction
Evolution of Biometric Security
Over the past few decades, biometric security has evolved remarkably, moving from basic signatures and fingerprint measurements to sophisticated technologies integrating facial recognition and iris scanning. This transformation mirrors advancements in computing and the growing demand for robust security methods, especially in an era marked by digital data breaches and identity theft. Notably, in the late 1990s, biometric systems were primarily used by law enforcement. Today, these systems are woven into various sectors, ranging from banking to mobile devices, enhancing security while streamlining user experiences.
Importance of Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication is not merely a trend; it has become essential in ensuring the safety of sensitive information. Its significance lies in several key benefits:
- Unique Identifiers: Each individual’s biometrics — like fingerprints or facial features — are unique, providing a higher level of security compared to traditional passwords.
- User Convenience: Users can quickly access systems with a simple touch or glance, eliminating the hassle of remembering multiple passwords.
- Reducing Fraud: Biometrics drastically cuts down on identity fraud, which costs businesses billions annually.
As we delve deeper into the facets of biometric security, it becomes clear that embracing this technology is not just beneficial but necessary in today’s digital landscape.

Basics of Biometric Technology
Definition and Types of Biometrics
At its core, biometric technology refers to the measurement and statistical analysis of people’s unique physical and behavioral characteristics. This technology empowers systems to identify or verify individuals based on their biological traits. Some common types of biometrics include:
- Fingerprint Recognition: Utilizing the unique patterns of ridges and valleys in fingerprints.
- Facial Recognition: Analyzing facial features, like the distance between eyes or the shape of the jawline.
- Iris Recognition: Capturing the unique patterns of the iris in the eye.
- Voice Recognition: Identifying individuals based on vocal characteristics and speech patterns.
Each modality offers distinct advantages, allowing users to select solutions tailored to their specific security needs.
How Biometric Systems Work
So, how do these systems actually function? When a user provides a biometric sample — like a fingerprint — the system performs the following steps:
- Capture: The sample is captured using a biometric sensor.
- Feature Extraction: Key features of the sample are extracted and converted into a digital code.
- Storage: This code is stored securely in a database.
- Matching: When the user attempts to authenticate, the system captures a new sample, extracts its features, and compares it against stored codes.
This process creates a seamless experience while ensuring high security, reinforcing the critical role of biometrics in modern technology.
Common Biometric Modalities
Fingerprint Recognition
Fingerprint recognition is perhaps one of the most widely used biometric modalities. This technology identifies individuals by analyzing the unique patterns of ridges and valleys on their fingertips. Nearly everyone has used it, especially on smartphones for unlocking devices or authorizing payments. For instance, one user shared how switching to fingerprint authentication made his daily routines much smoother — no more fumbling for passwords!
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition technology captures and analyzes facial features, allowing for quick identification. With advancements in artificial intelligence, systems can now process images in real-time. This modality is commonplace in social media platforms for tagging friends or in security systems that monitor public spaces. The accuracy of these systems has significantly improved, although they still contend with challenges like varied lighting and expression changes.
Iris Recognition
Iris recognition technology scans the colored part of the eye, which is unique to each individual. It boasts a high level of accuracy and is often used in high-security facilities. For example, airports have implemented iris scanning for expedited passenger verification, enhancing safety and efficiency.
Voice Recognition
Voice recognition analyzes vocal attributes to verify identity. It’s commonly used in virtual assistants like Siri and Google Assistant, enabling hands-free convenience. As one tech enthusiast noted, relying on voice commands has transformed how they interact with devices at home, making daily tasks feel more intuitive. Each of these modalities has its unique applications and advantages, demonstrating the versatility of biometric technology in enhancing security and convenience.

Advantages and Challenges of Biometric Security
Advantages of Biometrics
Biometric security systems offer several compelling advantages that make them increasingly popular across various industries. For instance, one major benefit is their enhanced security. Since biometric traits are unique to each individual, they significantly reduce the risk of impersonation or unauthorized access. Additional advantages include:
- Convenience: Users can access systems with a simple fingerprint scan or facial recognition, eliminating the hassle of remembering complex passwords.
- Efficiency: Biometric systems often allow for quicker verification processes, especially in high-volume areas like airports.
- Reduced Fraud: Organizations using biometric technologies experience fewer incidents of identity theft, which can be financially devastating.
Security and Privacy Concerns
Despite these benefits, biometric systems are not without their challenges. Security and privacy concerns remain hot topics of discussion. For example, while user data is typically encrypted, data breaches can still expose sensitive biometric information. Additionally, there are worries about:
- Surveillance: Some fear that widespread facial recognition applications may infringe on personal privacy.
- Data Misuse: Biometrics captured for one purpose could potentially be misused for others, shredding the trust users place in these systems.
Navigating these concerns is crucial as biometric technology continues to evolve. Engaging in dialogue around ethics and privacy is just as important as embracing the technological advancements.

Applications of Biometric Security
Biometrics in Mobile Devices
One of the most visible applications of biometric security is in mobile devices. Today, many smartphones come equipped with features like fingerprint scanners and facial recognition technology. This not only simplifies the unlocking process but also ensures secure transactions — like mobile banking. For instance, a user might find that using their fingerprint to approve payments makes online shopping not only faster but also significantly safer.
Biometrics in Law Enforcement
In law enforcement, biometrics play a crucial role in enhancing security and aiding investigations. Agencies use fingerprint and facial recognition systems to identify suspects quickly and accurately. Many police departments now employ body cameras with facial recognition software, allowing for real-time identification of individuals in public spaces. This has led to expedited investigations, although it’s essential to implement these systems thoughtfully to avoid privacy infringements.
Biometrics in Border Control
Border control agencies have also embraced biometric technology to streamline operations and enhance security. Systems featuring iris recognition or fingerprint scans expedite the authentication process for travelers. For example, travelers can enjoy smoother passage through security lines while ensuring stricter compliance with immigration laws. These advancements not only improve efficiency but also promote safety by enabling immediate identification of individuals on watchlists. As biometric security continues to expand across various sectors, its practical applications demonstrate both convenience and rigorous protective measures.

Future Trends in Biometric Security
Advancements in Biometric Technology
As technology continues to evolve, the future of biometric security appears promising and transformative. One significant advancement is the emergence of multimodal biometrics, combining two or more biometric traits for enhanced accuracy and security. For instance, imagine unlocking your phone by recognizing both your face and voice simultaneously — this not only increases security but also reduces the chances of false positives. Moreover, AI and machine learning are starting to play crucial roles in refining biometric systems. As these technologies analyze vast amounts of data, they improve recognition accuracy and speed. One tech enthusiast mentioned how their favorite app became even faster at recognizing their face after a recent update, showcasing the real-time improvements powered by AI.
Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies
However, with these advancements come potential risks. Cybercriminals may develop more sophisticated methods to circumvent biometric systems, leading to unauthorized access. To combat these threats, organizations should implement proactive mitigation strategies, such as:
- Regular updates and patches for biometric software to address vulnerabilities.
- User education on the importance of securing personal data, including their biometric information.
- Establishing strong data encryption protocols to safeguard stored biometric data.
As the landscape of biometric security continues to evolve, staying informed about risks and adopting preventive measures is essential for ensuring safety and privacy.
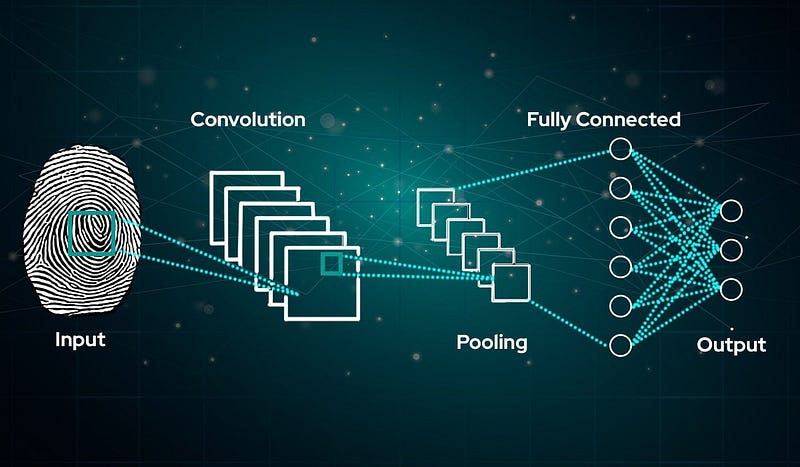
Implementing Biometric Security
Considerations for Implementation
When it comes to implementing biometric security, several key considerations must be addressed to ensure successful integration. First and foremost, organizations need to assess their specific security needs. For example, a banking institution may require higher-level authentication due to sensitive customer data, while a retail store might prioritize ease of access for staff. Additionally, factors such as budget, technological compatibility, and user experience should be considered. A user-friendly system encourages adoption, as observed when a local coffee shop switched to a fingerprint-based system, leading to faster customer service and happier patrons.
Best Practices for Biometric Deployment
To maximize the effectiveness of biometric deployment, following best practices is crucial. Here are some recommended strategies:
- Pilot Programs: Start with a smaller trial to identify potential issues before full-scale implementation.
- User Training: Offer comprehensive training sessions to ensure users are comfortable and familiar with the system.
- Data Protection: Establish strict protocols for storing and managing biometric data, including encryption and regular audits.
- Feedback Mechanism: Create channels for users to provide feedback on their experiences, allowing for continuous improvement.
By thoughtfully considering implementation factors and adhering to best practices, organizations can enhance security while fostering user trust and satisfaction.

Ethical and Legal Implications
Data Protection and Compliance
In the realm of biometric security, addressing data protection and compliance is crucial. With increasing regulatory scrutiny surrounding personal data, organizations must stay informed about laws such as GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California. These regulations mandate that individuals have rights over their biometric data and ensure organizations implement strict controls around its collection and storage. For instance, a technology firm recently faced penalties for storing biometric data without user consent — highlighting the importance of adhering to legal frameworks. Organizations should implement measures like:
- Transparency: Clearly communicate to users how their biometric data will be used and stored.
- User Consent: Obtain informed consent before collecting any personal data, emphasizing users’ rights to withdraw consent at any time.
- Regular Compliance Audits: Conduct audits to ensure ongoing adherence to legal requirements.
Ethical Use of Biometric Data
Beyond compliance, the ethical use of biometric data must be considered. Organizations need to carefully evaluate their motives for collecting biometric information. For example, the use of facial recognition in surveillance can lead to heated debates about invasion of privacy. It’s vital to ensure that biometric systems are implemented in ways that protect individual privacy and do not inadvertently support discrimination. Best practices for ethical use include:
- Minimization: Collect only the necessary biometric data for a specific purpose.
- Equity and Fairness: Ensure systems do not disproportionately impact marginalized groups.
- Public Discourse: Engage users and stakeholders in discussions about how biometric data is being used.
By focusing on these ethical considerations, organizations can foster trust while effectively using biometric technology in a rapidly evolving landscape.
Conclusion
Recap of Biometric Security Evolution
As we look back on the evolution of biometric security, it’s clear that this technology has transformed from simple fingerprint measurements to complex systems incorporating facial recognition and iris scans. Initially adopted primarily by law enforcement, biometrics have infiltrated everyday life, enhancing security in mobile devices, banks, and even airports. The increased reliance on this technology illustrates a growing societal trust in biometrics to protect sensitive information and streamline user experiences.
Future Outlook and Closing Thoughts
The future of biometric security is bright, but it is accompanied by rightful concerns regarding data protection and ethical use. Innovations like multimodal biometrics and AI-driven improvements promise increased accuracy and efficiency, yet the implementation must remain sensitive to privacy issues. Ultimately, fostering a dialogue about the ethical implications and compliance measures in biometric technology is essential. As individuals, we must remain vigilant about our data and advocate for responsible practices. With informed and ethical approaches, biometric security can pave the way for a safer, more convenient future, elevating both security measures and user confidence in digital interactions.
This article is written by Fady Azzi
Fady Azzi is a Cyber Security expert, based in Sydney, Australia. Through quick and short videos full of interesting and trusted information, Fady’s channel aims to inform and educate people of all ages about cyber security, hacking, technology and many interesting topics.

0 Comments