Navigating the Compliance Maze: Strengthening Cybersecurity Posture
Navigating the Compliance Maze: Strengthening Cybersecurity Posture
Introduction
Understanding Regulatory Compliance
Navigating the landscape of regulatory compliance can feel overwhelming for many organizations. Regulatory compliance refers to the need for businesses to adhere to laws, regulations, guidelines, and specifications relevant to their operations. In industries such as finance, healthcare, and information technology, maintaining compliance is not just about avoiding penalties; it’s vital for building trust with customers and stakeholders. For instance, consider a financial institution that fails to comply with the GDPR. The repercussions are not only financial fines but also a loss of credibility that can take years to restore.
Significance of Cybersecurity Posture
In the digital age, an organization’s cybersecurity posture is crucial. Cybersecurity posture encompasses the overall security status of an organization’s networks, devices, and data against cyber threats. A robust posture can:
- Deter potential cyber attacks
- Ensure data integrity and availability
- Facilitate compliance with regulations
Thus, understanding and enhancing your cybersecurity stance is an essential part of meeting regulatory requirements and safeguarding your organization’s future.
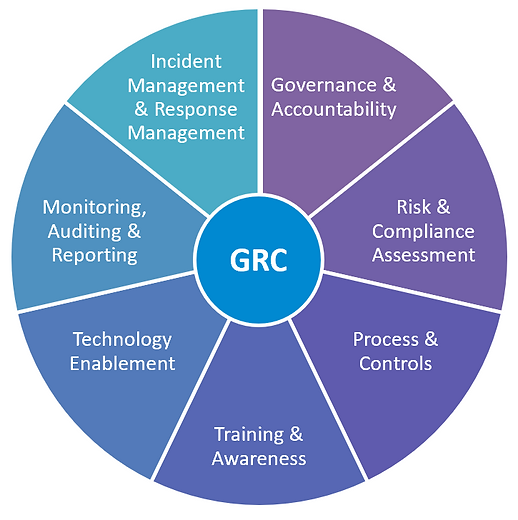
The Compliance Landscape
Overview of Regulatory Frameworks
As organizations strive to navigate the intricate web of regulatory compliance, it’s essential to understand the frameworks that guide adherence. Regulatory frameworks vary across industries but typically include guidelines from authorities like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). These frameworks provide the necessary structure for compliance, covering aspects such as:
- Data protection: Ensuring personal data is securely handled.
- Risk management: Identifying and mitigating potential threats.
- Reporting obligations: Requirements for disclosing breaches or incidents.
Compliance Challenges in Cybersecurity
Despite having frameworks in place, organizations often encounter significant compliance challenges in cybersecurity. One common hurdle is the ever-evolving nature of cyber threats that can render existing policies obsolete. Other challenges include:
- Resource constraints: Limited budgets and personnel to meet compliance demands.
- Lack of awareness: Employees may not fully understand compliance requirements.
- Integration issues: Aligning various IT systems with compliance standards can prove complex.
Organizations must address these challenges proactively to protect their data and achieve compliance effectively.

Building a Robust Cybersecurity Posture
Risk Assessment and Management
Transitioning from the compliance landscape, it’s vital for organizations to focus on building a robust cybersecurity posture. The first step in this journey is conducting thorough risk assessments. This involves identifying potential vulnerabilities and evaluating the risks they pose to your information systems. For example, a small marketing company might realize that outdated software used by employees is an entry point for cybercriminals. To effectively manage these risks, organizations should:
- Identify assets: List critical data and systems that require protection.
- Evaluate vulnerabilities: Determine potential threats and weaknesses.
- Prioritize risks: Focus on the most significant risks that could impact operations.
Implementing Security Controls
Once risks are assessed, the next step is implementing security controls tailored to mitigate these threats. Security controls are preventive measures designed to shield valuable assets. Effective strategies could include:
- Firewalls: Establish perimeter defenses to block malicious activity.
- Encryption: Protect sensitive data both at rest and in transit.
- Access controls: Limit who can view or edit critical information.
By addressing risks and strengthening security controls, organizations can significantly enhance their cybersecurity posture, ensuring compliance and safeguarding their future.

Compliance Audits and Assessments
Importance of Regular Audits
As organizations fortify their cybersecurity posture, conducting regular compliance audits becomes a critical component. These audits serve as a vital check-up, ensuring that policies and practices not only meet regulatory requirements but also align with business objectives. Regular audits can provide several key benefits:
- Early detection of issues: Identifying compliance gaps before they lead to serious breaches or penalties.
- Enhanced accountability: Promoting a culture of responsibility among employees regarding compliance.
- Informed decision-making: Providing data-driven insights that influence strategic planning.
For instance, a healthcare provider can discover through an audit that certain patient data access controls are insufficient, allowing them to address the issue proactively.
Effective Assessment Techniques
When conducting audits, employing effective assessment techniques is essential. Organizations might consider:
- Interviews and Surveys: Gathering insights from staff about compliance awareness and practices.
- Document Review: Regularly assessing policies, procedures, and training materials.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Using automated tools to identify and address potential weaknesses.
By implementing these assessment techniques, companies can ensure they not only comply with regulations but also foster an environment of continuous improvement in cybersecurity practices.

Incident Response and Compliance
Developing Incident Response Plans
Building on the foundation of thorough audits and assessments, organizations must also focus on incident response planning. An effective incident response plan (IRP) is crucial in mitigating the impact of security breaches. This plan should outline the steps to take when a cyber incident occurs, ensuring quick and efficient action. A well-rounded IRP typically includes:
- Identification: Recognizing a potential incident swiftly.
- Containment: Implementing measures to limit damage and prevent further harm.
- Eradication: Removing the cause of the incident.
- Recovery: Restoring systems and processes to normal operational status.
For example, a retail company might develop a response plan specifically addressing data breaches involving customer payment information, thus prioritizing protecting their customer trust.
Compliance Considerations in Incident Response
While developing an IRP, compliance considerations must remain at the forefront. Regulatory requirements often dictate how an organization should respond to incidents, including timelines for reporting data breaches. Organizations should ensure:
- Documentation: Keeping detailed records of incidents for compliance purposes.
- Notification Procedures: Establishing clear procedures for notifying affected parties and authorities in line with regulations like GDPR.
- Training: Regularly training staff on compliance-related aspects of the incident response process.
By thoughtfully integrating compliance into incident response, organizations enhance their resilience against cyber threats while ensuring adherence to legal and regulatory obligations.

Training and Awareness Programs
Educating Employees on Compliance
Following the implementation of incident response plans, an organization’s next focus should be training and awareness programs. Educating employees on compliance is essential for fostering a knowledgeable workforce that understands the importance of adhering to regulations. Training sessions can cover:
- Understanding Regulations: Familiarizing employees with relevant compliance frameworks such as GDPR or HIPAA.
- Identifying Risks: Teaching staff to recognize potential security threats, such as phishing scams.
- Best Practices: Sharing practical tips for handling sensitive data securely.
For example, a tech firm might host regular workshops to simulate phishing attempts, helping employees learn to spot and report these threats, thereby reinforcing compliance.
Promoting a Culture of Security
Beyond formal training, promoting a culture of security within the organization is crucial. This can involve leadership modeling compliance behavior and encouraging open communication about security issues. Strategies to cultivate this culture include:
- Regular Updates: Keeping staff informed about the latest security trends and compliance developments through newsletters.
- Recognition Programs: Acknowledging employees who demonstrate exceptional compliance practices.
- Collaborative Initiatives: Engaging teams in security drills or compliance competitions to make learning fun.
By entwining compliance education with a culture of security, organizations can create an environment where employees feel empowered to protect sensitive information proactively.

Continuous Compliance Monitoring
Tools for Monitoring Compliance
With a culture of security established, the next step in the compliance journey is continuous monitoring. Leveraging the right tools can significantly enhance an organization’s ability to maintain compliance in real-time. Various compliance monitoring tools are available to help organizations streamline this process. Key tools include:
- Compliance Management Software: These platforms track regulatory changes and assess compliance levels, providing alerts for any discrepancies.
- Automated Auditing Solutions: Automating the auditing process can save time and reduce human error, making audits more efficient.
- Vulnerability Scanners: These tools regularly scan systems for vulnerabilities, helping organizations address issues before they escalate.
For instance, a healthcare provider might use automated auditing solutions to comply with HIPAA regulations, ensuring ongoing adherence without the administrative burden.
Integrating Compliance into Daily Operations
To truly achieve continuous compliance, it’s essential to integrate compliance requirements into daily operations. This approach can involve:
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Creating SOPs that align with regulatory requirements can guide employee actions and decision-making.
- Regular Training Sessions: Integrating compliance-focused training into employee development programs ensures that compliance remains a priority.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Encouraging collaboration between departments can foster a comprehensive understanding of compliance across the organization.
By incorporating compliance monitoring and practices into everyday operations, organizations can proactively manage regulatory obligations and mitigate risks, ensuring smooth functioning and long-term success.

Future Trends in Compliance and Cybersecurity
Emerging Technologies
As organizations bolster their cybersecurity measures, it’s essential to stay attuned to future trends in compliance and cybersecurity. One major trend is the adoption of emerging technologies that can transform how compliance is approached. Technologies like:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can analyze vast amounts of data to identify potential compliance breaches or security threats before they escalate.
- Blockchain: This technology ensures data integrity and traceability, making it an effective tool for demonstrating compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Cloud Computing: As more organizations transition to the cloud, they must adopt new compliance frameworks tailored specifically for cloud environments.
For example, a financial institution might implement AI tools to monitor transactions for unusual patterns, automating compliance checks and improving efficiency.
Evolving Regulatory Landscape
Alongside technological advancements, the regulatory landscape continues to evolve. Governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on stricter compliance measures, especially in sectors like finance and healthcare. Organizations will need to adapt to:
- Increased Transparency Requirements: Regulations may mandate more detailed disclosures regarding data management practices.
- Global Compliance Standards: As businesses expand internationally, navigating various global compliance regulations will become more complex.
By being aware of and adapting to these emerging technologies and evolving regulations, organizations can enhance their compliance strategies, ensuring they remain not only compliant but also resilient against future threats.

Conclusion
Recap of Key Strategies
As we wrap up our discussion on compliance and cybersecurity, it is crucial to recap the key strategies that have been highlighted throughout our journey. Organizations can strengthen their compliance and cybersecurity frameworks by implementing these approaches:
- Conduct Regular Risk Assessments: Understanding vulnerabilities helps in prioritizing security measures effectively.
- Develop Comprehensive Incident Response Plans: Being prepared for incidents ensures timely and effective responses.
- Engage in Continuous Compliance Monitoring: Utilizing tools for real-time monitoring can preempt compliance issues before they escalate.
- Foster a Culture of Security: Training employees and establishing a security-first mindset is fundamental for long-term success.
Final Thoughts on Strengthening Cybersecurity Compliance
In the ever-evolving landscape of compliance and cybersecurity, organizations must be proactive rather than reactive. By staying informed of trends and technologies, businesses can better navigate the complexities of regulations while safeguarding their information assets. For instance, having a culture that promotes vigilance against cyber threats can significantly enhance an organization’s resilience. In summary, investing in robust compliance strategies paves the way for sustainable success, driving both security and trust in an increasingly digital world.
This article is written by Fady Azzi
Fady Azzi is a Cyber Security expert, based in Sydney, Australia. Through quick and short videos full of interesting and trusted information, Fady’s channel aims to inform and educate people of all ages about cyber security, hacking, technology and many interesting topics.

0 Comments